Page One - Graydon
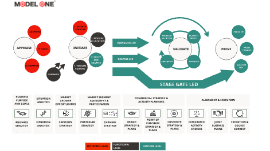
Transcript: eDiscovery & Forensics eDiscovery Definition eDiscovery definition (often referred to as ESI, or, “Electronically Stored Information”): Electronic discovery refers to any process in which electronic data is sought, located, secured, and searched with the intent of using it as evidence in a civil or criminal legal case. (Will soon just be, “Discovery”.) eDiscovery Definition History How did it begin? Old way of Discovery vs. incorporating technology. How does this make better lawyers / better law firms? What is the EDRM? What is the EDRM? Redden Matter Information Governance Information Governance Getting your electronic house in order to mitigate risk & expenses should eDiscovery become an issue, from initial creation of ESI (electronically stored information) through its final disposition. *Culling down data before even getting going* Locating potential sources of ESI & determining its scope, breadth & depth. Data Mapping (Where is everything?) Identification Identification Ensuring that ESI is protected against inappropriate alteration or destruction. LEGAL HOLDS, BABY! Legal Holds ensure data cannot be destroyed. Failure to preserve can lead to sanctions. Preservation Preservation Gathering ESI for further use in the e-discovery process (processing, review, etc.). Transferring data from a company to their legal counsel. Sometimes Digital Forensics may be used for collections (cell phones, texts, social media, etc.) Collection Collection Digital copies / collections of the following: Digital Forensics *Cell Phones (Android Issues) *Laptops *Social Media / Ephemeral Data Reducing the volume of ESI and converting it, if necessary, to forms more suitable for review & analysis. Deduplication and de-Nisting come into play. Processing Processing Evaluating ESI for relevance & privilege. (What've we got here?) Review Review Evaluating ESI for content & context, including key patterns, topics, people & discussion. Analysis Analysis Delivering ESI to others in appropriate forms & using appropriate delivery mechanisms. Production Production Displaying ESI before audiences (at depositions, hearings, trials, etc.), especially in native & near-native forms, to elicit further information, validate existing facts or positions or persuade an audience. Presentation Presentation Cloud-Based / Not land-locked programs. Really, how does it work? Really, how does it work? Speed, baby! Creative edits without worry of spoliation Mistake made? Start over. Share w/Colleagues through the magic of the web. Electronic Atmosphere is Magic Used Correctly, can help compete on level grounds. NYC vs. Indy vs. Cincy vs. Louisville vs. Lexington Market / Who's In? Market / Who's In? Where are you in the industry with your ESI education? Are your members satisfied? Are you utilizing technology to grow your firms' business? Fear of technology? Honest Questions: Honest Questions: In-House Vs. Farming it Out. Options for Law Firms Options for Law Firms Pros: Control all data. Only 1 cost per year. No middle-man. Cons: Security burden. Cost demands workflow. Latest and Greatest Tools and Analytics. Co-Counsel's other platforms. In-House In-House Pros: Pricing Per Matter or MSA options. May be able to pass through to clients. Data hosted elsewhere = less security risk. No Licensing / Software fees. Latest and Greatest! Cons: Using a middle-man. Possible Communication issues between parties (#1 complaint). Farming it Out Farming it Out How does this make you better lawyers / How does this make your firm a better firm? Why?? Why?? Story #1 "$100,000 Firing" Story #2 "Uncommon Growth" Clients are no longer going to use the old system and tolerate firms that are inefficient with their law practices. Speed, Efficiency and Security Speed, Efficiency and Security Talented Superstars on the rise are attracted to firms that embrace technology and grow because of it. Modern Firms are Sexy / Grow Much Faster Modern Firms are Sexy / Grow Much Faster Questions so far? Halftime! Halftime! Platforms What Platforms are out there? Relativity Xera LogicKull NextPoint IPRO CasePoint Summation Platforms Do they work well together? (NO!) Analytics added in. Pricing (We'll get to that) Differences? Differences? Emerging Trends / Tools and Analytics Emerging Trends / Tools and Analytics T.A.R. (Technology Assisted Review) - Sometimes called Predictive Coding NexLP - Actually measures emotional intelligence in the batch Brainspace - Tool to make review as aesthetically pleasing as possible to reviewer based on patterns. A.I. (How Skynet Starts) A.I. (How Skynet Starts) Pricing How do Service Providers make money? Law firms are conditioning their clients to get used to this expense. This efficiency is cost of doing business. What about pass-throughs to the clients and how does that work? Pricing Processing fee Workstation fee Custodian fee Hosting fee Production fee (often based on hourly rate) Common Charges Common Charges Ingestion fee Training fee Cold Storage fee ESI