Nike Presentation
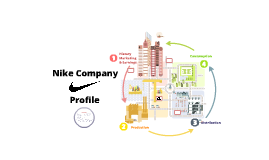
Transcript: •Plan - At the core of our business is a plan – our opportunities, our resources and our values. It’s who we are. What we believe. And how we get things done. •Design - Form. Function. Superior performance. Minimal impact. While our designers always strive to create products that are faster, lighter and stronger, they also pay close attention to smarter. •Make - Ideas don’t become reality by magic. For a global business, it requires people, materials, tools, knowledge, skill and a whole lot of coordination. We contract with more than 900 factories globally to make products from our designs. •Move - We ship products wherever and whenever they are needed, to get to thousands of partners and millions of consumers around the world. Airplanes, boats, trucks and trains are the tools our transport providers use to overcome the obstacle of distance every day. •Sell - Nike operates more than 750 retail stores around the world across all our brands. Beyond selling products, each location strives to be a rewarding experience for its consumers and an asset to its community. The stores are in leased space. While NIKE and our Affiliate brands sell primarily through retail partners not owned by our company, our focus is on the impact of the selling we do in our own stores. •Use - Once you bring home your new shoes, shirt or shorts, a different footprint starts to take shape. This one belongs to you. Reuse - Finding innovative ways to reuse our products – creating running tracks, sport courts and even new shoes and clothing helps minimize our impact on the environment. Good becomes better over time. And so do we. NIKE, Inc. includes seven distinct brands, each with a powerful connection to its customers: •NIKE Brand •Cole Haan - luxury apparel and accessories. •Converse •Hurley International LLC •Umbro •Nike Golf •Jordan Brand They think of it less as a chain, and more as “something that is actually interconnected in multiple ways, like an ecosystem or a web… The connections in this chain drive our decision making… Each choice has financial, environmental and social impacts that are intertwined and mutually dependent.” Mark Parker has been the third Chief Executive Officer of Nike, Inc. since 2006. Began at Nike, Inc. in 1979. For more than 30 years, he’s brought innovative concepts and engineering expertise As CEO he is responsible for the growth of NIKE, Inc.'s global business portfolio, which includes Converse Inc., NIKE GOLF, Cole Haan, and Hurley International LLC. Other Executives: Philip H. Knight - Chairman of the Board of Directors Charlie Denson - Preseident of the Nike Brand CEO - Leadership Style Suppliers do not have strong bargaining power toward Nike; on the contrary, Nike is able to be selective. Vision: Approximately 120 million shoes sold per year. External Analysis To bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete* in the world. *If you have a body you are an athlete. "We identify qualified suppliers through our bid process which includes market research and analysis online, benchmarking with other companies, referrals from other companies and research services." "Nike requires a broad base of suppliers that actively and significantly support our business requirements, and positively reflect the world in which we live and work." "Supplier Diversity can have a favorable impact on our business by: •Creating more competition in the supply chain •Maintaining a connection to the consumer base •Providing economic stimulus to the community •Contributing to the enhancement of our brand" RIVALRY General Information Financial - Side by sides: Innovation and Sustainability: Nike is committed to helping create a sustainable future. It sees this as the future of business and so it sees sustainable strategies as not only good for the earth and its resources but also for their business. This shapes many parts of Nike's strategy and decisions. Innovation and creativity to find new ways of making products, new product designs (for better performance as well as for more sustainable methods of production). "Disruptive innovation" is needed to make more progress in sustainability. Nike has a matrix organization. In a matrix organization, employees report to project or product teams led by a product manager as well as to the department manager. With Nike, each brand has a department, and each department makes decisions independent of the CEO. Each department also has sub-departments or project teams responsible for handling mini-tasks within each department. Nike has 750 stores all over the world, operating in leased spaces, but the majority of its sales are through other retailers not owned by Nike. The large number of possible vendors could improve Nike's bargaining position by competition between these retailers, but the fact that most of Nike's sales are through these stores, and that they are therefore needed by Nike, gives these retailers more bargaining power as well. Furthermore, the competition for low prices