Homeowner Presentation
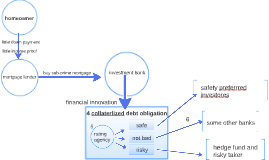
Transcript: Federal Aid and Policies for Homeowner and Homebuyers The housing market was originally intended for home buyers who were able to secure a loan. This meant people able to pay for the duration of the loan each month. In 2004, the US economy was booming, making money easily available and allowing everybody to obtain a loan. Including people known as NINJA borrowers (No Income, No Assets or Job). At this point even banks were happy to be giving away money because it was widely believed that housing prices were going to continue to grow forever. This same thinking caused many people that were on the fence about purchasing a house to go ahead and do so, fearing that if they waited they would not be able to afford it. This huge demand caused housing prices to soar, making the housing market more and more lucrative. Suddenly, in 2007 the bubbled bursts and the housing market collapsed. Unemployment increases and more and more loans go unpaid each month. The housing market stops being a great investment and the money supply is quickly cut off. Millions of homeowners owe more on their homes than the loan they took from the bank and as these loans are not paid the homes go into foreclosure. Banks begin selling these foreclosed homes at much lower prices that originally paid causing both prices and demand to decrease. At the same time, supply is finally catching up with the demand and prices from before. This creates a massive surplus of houses newly constructed and housing that went into foreclosure. This leaves millions of people in homes that they can no longer afford and that are decreasing in value each day with their loan payments SOLUTIONS Keynesian Resurgence Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008 commonly referred to as a bailout of the U.S. financial system, is a law enacted in response to the subprime mortgage crisis authorizing the United States Secretary of the Treasury to spend up to US$700 billion to purchase distressed assets, especially mortgage-backed securities, and make capital injections into banks . "We must... avoid a continuing series of financial institution failures and frozen credit markets that threaten American families' financial well-being, the viability of businesses both small and large, and the very health of our economy." -Treasury Secretary Henry Paulson summarized the rationale for the bailout to US Senate Economic Stimulus Act of 2008 The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act ARRA The objective for ARRA was to save and create jobs almost immediately. Secondary objectives were to provide temporary relief programs for those most impacted by the recession and invest in infrastructure, education, health, and ‘green’ energy. The approximate cost of the economic stimulus package was estimated to be $787 billion at the time of passage. The Act included direct spending in infrastructure, education, health, and energy, federal tax incentives, and expansion of unemployment benefits and other social welfare provisions. Home Buyer Tax Credit Privides up to $8,000 for some first-time home buyers. The law also adds a new tax credit of up to $6,500 for certain repeat home buyers. The package, which the government estimates will cost a total of $11 billion, is intended to help spur housing sales, a critical part of the economy Federal Mortgage Assistance Programs Special refinancing program: Homeowners with more than 20 percent equity in their home can refinance their mortgage at today's low rates and decrease their monthly payment by hundreds of dollars.But people whose home values have dropped significantly often have a tough time finding a lender that will refinance their mortgage, especially if they owe more than 80 percent of their home's current value. This special program will help those people refinance into cheaper loans. To qualify, your loan must be owned or guaranteed by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac, and you must not have missed any loan payments in the past 12 months. Loan-modification program: This program is designed to help people who are struggling to make mortgage payments. The government will provide incentives for lenders to lower borrowers' monthly mortgage payments to 31 percent of their gross monthly income, either by lowering the interest rate to as little as 2 percent or by extending the terms of the loan up to 40 years. Federal Mortgage Assistance Programs: HARP Home Affordable Refinance Program: This program is basically meant for home owners whose mortgages have depreciated in value in the recent times, and the collateral fails to provide enough financial guarantees for the existing mortgage. The End Housing Bubble Principal Actors HAMP Home Affordable Modification Program The main objective of HAMP is to modify or restructure the terms and conditions linked with your current mortgage and make the monthly mortgage payments more affordable. An Act of Congress providing for several kinds of economic stimuli intended to boost the United States economy in 2008 and to