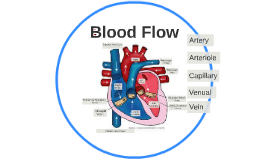
Blood Flow Powerpoint
Transcript: The two chambers that are associated with the pulmonary circuit are the right atrium and the right ventricle. 16.Explain what would happen if a branch of a coronary artery were to become blocked. The blockage of a oronary artery would lead to a restriction of blood flow to the demands of the active cardiac muscle. Oxygen: Turns deoxygenated blood into oxygenated blood so it can be used where it is needed throughout the body. Pulmonary veins: Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs torwards the heart. Left atrium: Collects blood from the pulmonary circuit. Bicspid/Mitral Valve: The papillary muscles contract which tenses the chordae tendineae, resulting in limited movement of the cusps, and preventing backflow. Left Ventricle: Ejects blood into the systemic circuit. Aortic Semilunar Valve: Gaurds the entrance to the aorta once the left ventricle is filled, then it opens to allow blood to flow to the aorta. Aorta: Pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. Systemic System: Transports blood to and from the rest of the body. (Starting and ending at the heart). 13. What valves prevent backflow from aortic/pulmonary trunks into ventricles. The aortic semilunar valves valves prevent backflow from aortic/pulmonary trunks into ventricles. Into the left ventricle. 2. What prevents the AV valves from swinging into the atria? Where the blood then flows through the (mitral) bicuspid valve. The two chambers associated with the systemic circuit are the left atrium and the left ventricle. 14. Define pericarditis. Pericarditis is the inflammation of the pericardium. Functions: 20. Explain the signs/symptoms of agina pectoris. The signs of agina pectoris may include the blockage of 1 or more arteries/ coronary heart diasese. Symptoms of agina pectoris include: chest pain, fatigue, dizziness, and the inability to excercise. The blood then empties up through the inferior and superior vena cava back into the right atrium. Red= Oxygenated blood Blue= Deoxygenated blood When the ventricles contract, the AV valves are closed, and the SL valves are open. Damage to the semilunar valve on the right side of the heart would affect blood flow to the pulmonary trunk. Superior vena cava: Delivers doxygenated blood from the upper body, head, neck, etc. Inferior vena cava: Carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body, lower limbs, etc. Right Atrium: Receives blood from the systemic circuit. Tricuspid valve: The papillary muscles contract which tenses the chordae tendineae limiting the movement of the cusps and preventing backflow. Right Ventricle: Discharges blood into the pulmonary circuit. Pulmonary semilunar valve: Guards the entrance to the pulmonary trunk. Once the Right ventricle is filled, the pulmonary semilunar valve opens to allow blood to flow to the pulmonary arteries. Pulmonary Arteries: Send blood to the lungs and away from the heart. Lungs: Gas exchange occurs to convert carbon dioxide into oxygen. The blood then travels through the aorta where the blood then leads to all of the arteries of the body. 5. What role do the chordae tendineae and papillary muscles play in the normal function of the AV valves? 3. Why is the left Ventricle more muscular than the right ventricle? The role the chordae tendineae and papillary muscles play in the normal function of AV vales is during ventricular contraction, tension in the Papillary muscles pull against the chordae tendinae, which keep the cusps of the AV valve from going into the atrium. This action prevents the backflow of blood in to the atrium as the ventricle contracts. When ventricles relax, AV valves are open and the SL valves are closed. Chordae tendineae are loose and the papillary muscles are relaxed. Into the lungs, where the blood then becomes oxygenated. By: Victoria Skoney Up into the pulmonary arteries. The blood then goes to the body, arms, legs, brain, and organs.This is where the blood becomes deoxygenated. The veins from the entire body bring deoxygenated blood back to the heart. The more muscular left ventricle must generate enough force to propel blood throughout the body (except the lungs), whereas the right ventricle must generate only enough force to propel blood to the short distance to the lungs. Contraction of the papillary muscles pulls on the chordae tendineae, which prevent the AV valves from swinging into the atria. Questions: The causes of mitral valve prolapse could be 1 or both mitral cusps that have extra tissue bulging into the left atrium ech time the heart contracts: which causes regurgitation. 19. Heart murmurs are detected more/less frequently in the elderly? Heart murmurs are detected less frequently in the elderly. Through the pulmonary semilunar valve. 4. What are the causes of mitral valve prolapse? 9. What are the two chambers associated with the systemic circuit? The cause of arteriosclerosis could include: smoking, high blood pressure, obesity, and other factors that accumulate to plaque buildup. Symptoms may include chestpain,