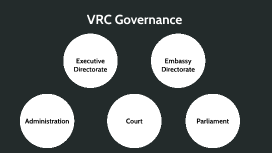
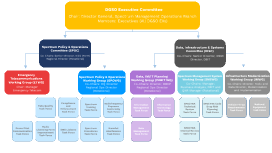
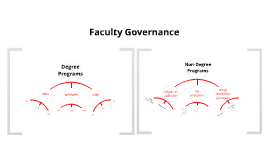
Governance Structure
Transcript: The offical languages of Morocco are Arabic and French Islam is the main religion followed Arabic dialect, Derija is most widely spoken The culture is "deeply rooted" in Islam Moroccans traditions value family, honor, dignity, generosity, hospitality, and self-control Post-colonial Language, Culture, and Religion Europeans were attracted to the location and resources of Morocco The industrialization of the Europeans made it easier to invade and rule French and Spain wanted to conquer Morocco They had an agreement to divide Morocco into two zones of French and Spanish influence in 1904 Post-colonial Colonial Bibliography Colonial Colonial Pre-colonial Pre-Colonial Cities were located by the rivers or by the coast for easy access of transportation and trade Morocco was a rich agricultural land Pre-colonial 1956 Morocco became an independent country 2011: a new constitution was created It lessened the power of King Muhammad VI and strengthened the power of the prime minister Spain took control of the far north and south of Morocco France took control of central Morocco Bibliography Fact Monster. Last modified 2008. http://www.factmonster.com/ipka/A0107800.html. Geographia. Last modified 1998. Accessed 2005. http://www.geographia.com/morocco/. Madar, Anuja, ed. Frommer's Morocco. Frommer's. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2010. The Political and Economic History of Morocco. http://www.sjsu.edu/faculty/watkins/morocco.htm. World Travel Guide. Accessed 2014. http://www.worldtravelguide.net/morocco/history-language-culture. Morocco was in demand for its agricultural land, location, and resources Post-Colonial Morocco Royal Moroccan Forces were founded in 1956 after the independence of Morocco from Spain and France Geography and infrastructure In 1956 Morocco became free from France's rule (left a great influence on culture) Spanish and French were a secondary language Religion: Christianity, jewish, and Islam Governance Structure Colonial Post-Colonial By Jessica Whetzell Pre-Colonial Today Morocco employs 45% of labor force Morocco's industries: Food processing, Leather goods, Textiles, Construction, and Tourism Morocco has the world's third largest deposite of phosphate (20% of export earnings) Issues: high unemployment and illeteracy Morocco is located in northwest of Africa 102,703 Square miles Issues: Soil erosion, over-grazing, destruction of habitat and water supply contaminated by raw sewage 1912: Morocco established an army made up of a Makhzen Army (only the higher ranked people were able to join) and the Berber militias. The Berber militias had the abilities to withstand the French and Spanish for over 30 years. Morocco was under the control of the Berbers since 2nd millennium B.C. Many conflicts between the Berbers and the Arabs Arabs introduced Moroccans to the dynasty ruling power In the 15th century Spain and Portugal were fought off The pressure of imperialism grew for Morocco Colonial Spain and France had interest in Morocco for: Trade Mineral wealth Fertile land Pre- colonial 1912-1956 a great number of Moroccans were enlisted to serve for the Spahi and Tirailleurs of the French army In 685 Arabs invaded Morocco and brought the religion of Islam Arabs brought the ruling dynasty system to Morocco Morocco's Culture had a mix of Berber, Mediterranean, Andalusian, and african traditions The famous prophet Muhammad came from the Alawite Dynasty in 1660 Armed Forces/ Military Economy Post-Colonial