Lung
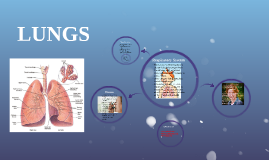
Transcript: Lung cANCER The 2 main types of lung cancer are: Non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer. It grows more slowly than small cell lung cancer. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) grows quickly and often spreads to distant parts of the body. Stages Stage I: The cancer is located only in the lungs and has not spread to any lymph nodes. Stage II: The cancer is in the lung and nearby lymph nodes. Stage III: Cancer is found in the lung and in the lymph nodes in the middle of the chest, also described as locally advanced disease. Stage III has two subtypes: If the cancer has spread only to lymph nodes on the same side of the chest where the cancer started, it is called stage IIIA. If the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes on the opposite side of the chest, or above the collar bone, it is called stage IIIB. Stage IV: This is the most advanced stage of lung cancer, and is also described as advanced disease. This is when the cancer has spread to both lungs, to fluid in the area around the lungs, or to another part of the body, such as the liver or other organs. Risk Factors Smoking tobacco Second-hand smoke Radon Asbestos Outdoor air pollution Occupational exposure to chemical carcinogens Personal or family history of lung cancer Arsenic Previous lung disease Exposure to radiation Indoor burning of coal Weakened immune system Lupus sIGNS & SYMPTOMS a cough that worsens or doesn’t go away chest pain that is constant and made worse by deep breathing or coughing blood-stained sputum (mucus and other matter coughed up from the lungs) shortness of breath wheezing frequent chest infections (bronchitis or pneumonia) fatigue hoarseness loss of appetite weight loss collapsed lung (pneumothorax) Late S & S's buildup of fluid around the lungs (pleural effusion) bone pain jaundice difficulty swallowing superior vena cava syndrome neurological changes weakness headache numbness in a limb dizziness seizure enlarged lymph nodes in the neck or above the collarbone Treatment surgery chemotherapy radiation targeted therapies photodynamic therapy Alternative Medicine Anxiety : Hypnosis, massage, meditation, relaxation techniques Fatigue : Exercise, massage, relaxation techniques, yoga Nausea and vomiting : Acupuncture, aromatherapy, hypnosis, music therapy Pain : Acupuncture, aromatherapy, biofeedback, hypnosis, massage, music therapy Sleep problems : Exercise, relaxation techniques, yoga Stress : Aromatherapy, exercise, hypnosis, massage, meditation, tai chi, yoga Stigma Many lung cancer patients, whether they smoked or not, feel particularly stigmatised because the disease is so strongly associated with smoking. In fact, as many as 15% of lung cancer patients are life-long non-smokers, and 50% of patients diagnosed with lung cancer have quit before the time of diagnosis. The association of lung cancer with smoking often results in negative reactions and blame from others, assuming those patients ‘brought it upon themselves’. The IP TEAM Anesthesiologist Dietitian Family doctor Nurse Occupational therapist Oncologist Oncology nurse Pathologist Patient advocate Pharmacist Physiotherapist, Psychologist Radiologist Social worker Spiritual care worker Surgeon Technical staff psw role post surgery (personal care) observe and report changes support (emotional, sOCIAL, physical) check vitals (delegated) turn on oxygen tank Support Canadian Cancer Society hopespring.ca sOURCES CANADIAN CANCER SOCIETY CANADIAN LUNG ASSOCIATION MOSBYS TEXTBOOK FOR THE psw end