White Blood Cells
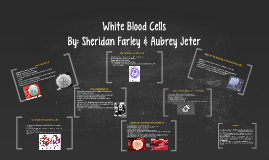
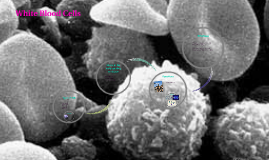
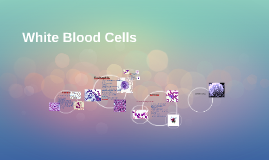
Transcript: there are many different types of white blood cells white blood cells can determine if you may have a disease help with our immune system colorless and have an irregular shape very different from red blood cells the amount of white blood cells in every drop of blood is lower than we thought What are diseases that affect white blood cells? A consistently high count of white blood cells is a sign of Leukemia. If an infection fights back and persists the number of white blood cells increases. The amount of white blood cells determines if there is a disease. Lymphocytes have a large nucleus and little cytoplasm Nucleus appears large under cell division Round with a dip in the middle Irregular shape, but usually circle or oval They don't have a specific shape so that they can surround and destroy the bacteria in your body. Comparing and Contrasting with a Red Blood Cell White blood cells a.k.a leukocytes Cells of the immune system Found in blood & the lymphatic They have a short life-lasting from a few days to a few weeks Produced from a hematopoietic stem cell in bone marrow Most are formed in bone marrow Drop of blood has an average of 7000 white blood cells Types of white blood cells " Respiratory & Cardiovascular Physiology." Bristol UWE - Faculty of Health and Life Sciences. N.p., n.d. Web. 18 Oct. 2013. <http://hsc.uwe.ac.uk/rcp/cs-blood-structure.aspx>. Bianco, Carl, and MD. "HowStuffWorks "White Blood Cells"." HowStuffWorks "Science". N.p., n.d. Web. 18 Oct. 2013. <http://science.howstuffworks.com/life/human-biology/blood2>. "Blood: White Blood Cells - The Human Heart: An Online Exploration from The Franklin Institute, made possible by Unisys." The Franklin Institute - Home - 215.448.1200 . N.p., n.d. Web. 18 Oct. 2013. <http://www.fi.edu/learn/heart/blood/white.html>. "White blood cell - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia." Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 18 Oct. 2013. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/white-blood-cell>. What is a white blood cell? Works Cited White blood cells are larger than red blood cells. Red blood cells don't have a nucleus; White blood cells have nucleus White blood cells are colorless, but red blood cells are red Both are required for the function of the body Red blood cells carry oxygen; White blood cells fight off bacteria Average of 5 million red blood cells in a drop of blood, but only an average of 7 thousand white blood cells in a drop of blood Red blood cells live for about 120 days; White blood cells live a few days to a few weeks Red blood cells are round and can change shape without breaking; White blood cells have different shapes and can multiply easily, but can't change shape. VS. White Blood Cells By: Sheridan Farley & Aubrey Jeter What we retained about white blood cells from this project Neutrophil: accounts for 58% of cells in the blood and targets bacteria and fungi Eosinophils: 2% in the blood, targets larger parasites and modulates allergic inflammatory responses Basophil: 1%, releases histamines for inflammation responses Lymphocte: 4% , B cells release antibodies and help the activation of T cells, T cells activate and regulate T and B cells, large nucleus, little cytoplasm Monocytes: 4%, move from bloodstream to differentiate tissues Defends the body against infectious diseases and foreign materials Attack germs- some are positive antibodies that overpower the germ while others surround and destroy the bacteria During cell division genetic material is doubled What is the structure of a white blood cell? What are the functions of the white blood cells?