Mrs.Moreland Ecosystem Rubric powerpoint
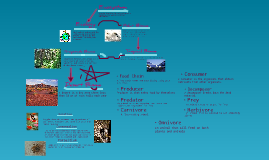
Transcript: Ecosystem Project Taiga Location The taiga is the largest biome. The taiga is primarily a coniferous forest (evergreen trees with needles) like the temperate rainforest, but the taiga is located between 50 degrees latitude north and the Arctic circle. Many coniferous trees (evergreens with needles) grow in the taiga. The taiga has fewer animal species than the tropical or temperate deciduous forests. The taiga climate is for the most part dominated by cold arctic air. Exceptionally cold winds bring bitterly cold air from the Arctic Circle: the temperatures fall even more on clear nights when there is no cloud cover. Because of earth's tilt, the taiga is turned away from the sun in the winter. Less of the sun's radiation reaches the ground to warm it up. Winter, with it's freezing cold temperatures, lasts for six to seven months. Summer is a rainy, hot and short season in the taiga. Fall is the shortest season for taiga. Spring brings flowers, the frozen ponds melt, and the animals come out from hibernation. The summers are mostly warm, rainy and humid. They are also very short with about 50 to 100 frost free days. The total precipitation in a year is 30 - 85 cm (12 - 33 in) . The forms the precipitation comes in are rain, snow and dew. Most of the precipitation in the taiga falls as rain in the summer. The main seasons in the taiga are winter and summer. The spring and autumn are so short, you hardly know they exist. It is either hot and humid or very cold in the taiga. The typical taiga soil is called podzol or podsol. It has a dark upper horizon (A) this layer is dark because it's rich in humus formed from decomposition of the leaf litter. Horizon A is followed by a characteristic lighter (whitish) eluvial horizon (E) the mineral components of this layer have drained toward the deeper, usually brownish B horizon. The B horizon overlays the broken down rock (C horizon). Paper Birch Fire Snag Willow Wild Rose Trembling Aspen Tamarack Bobcat Bald Eagle Gray Wolf River otter Wolverine red fox THE END YEAHHHH Ecosystem rubric In the taiga, the average temperature is below freezing for six months of the year. Total yearly precipitation in the taiga is 12 - 33 inches (30 - 85 centimeters). Although the cold winters have some snowfall, most of the precipitation comes during the warm, humid summer months.Because of the tilt of the earth on its axis, in the taiga you'll find long nights in the winter and long days in the summer. During the summer months, the taiga fills up with millions of insects. Birds, who eat insects, migrate every year for the plentiful food supply. The taiga is prone to wildfires. Many trees have adapted to this by growing thick bark, which can protect a tree from a mild fire. Temperature Taiga Additional Notes Mrs.Moreland Melody Land 1st Period Climate Taiga Because of cold temperatures, decomposition is slow in the taiga. Dead vegetation will pile up on the forest floor, making a sponge-like covering. Since decomposition is slow, the soil is thin, and lacking in nutrients. Trees grow taller where the taiga is warmer (so things can decay) or by a stream, where the water can carry nutrients to the tree. The world's oldest trees can be found in the taiga. The bristlecone pines in California are a prime example. One of them is 4,600 years old . Soil Description Precipitation 6 Animals in Taiga Taiga Mrs.Moreland Melody Land 1st Period Taiga 6 Plants in the Taiga