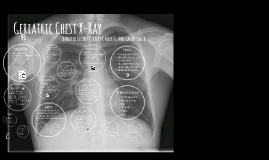
Geriatric Chest X-Ray
Transcript: Pregnancy may be asked if the patient is 55 or younger (No usual for geriatric pts.) What is the exam? History questions Pathology Able to stand on their own Upright imaging Wall bucky set up Line up patient Shield Set technique Take images 1. What is the centering point for a Chest x-ray? 2. Name 2 possible diseases seen on a Chest x-ray. 3. What prep does the patient need to do for this exam? 4. What technique should be used? 5. What changes the technique? Position patient for lateral projection- Left side on board, arms above head or holding on to bars provided, keep feet straight forward, no rotation Set technique for patient Give breathing instructions and take image Make sure patient has all of their things and they are free to go Walk them back to where you got them Techniques Complete exam details May or may not be able to stand Keep in chair or cart if not Wheelchair- set up like upright on wall bucky. Cart- Use free detector Position patient Use positioning sponge for lateral Set technique Take images Eisenberg, R. L., Johnson, N. M., & Eisenberg, R. L. (2011). Respiratory System. In Comprehensive radiographic pathology, sixth edition. Frank, E. D., Long, B. W., Smith, B. J., Merrill, V., & Ballinger, P. W. (2007). Thoracic Viscera. In Merrill's atlas of radiographic positioning & procedures. St. Louis, MO: Mosby/Elsevier. Geriatric Radiography. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.hkrta.50g.com/Academicdoc/Geriatric.pdf Gossner, J., & Nau, R. (2013, July 1). Geriatric Chest Imaging: When and How to Image the Elderly Lung, Age-Related Changes, and Common Pathologies. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3713368/ What you Need to Know About Chest Radiology. (2009). Retrieved from https://www.asrt.org/docs/default-source/patientpages/chest_papg.pdf?sfvrsn=4 1. T7 or Bottom of scapula 2. COPD, Pneumonia, CHF, ECT. 3. None 4. 90-125kVp 1-3 mAs 5. Patient size and Pathology (additive or destructive diseases) Exam Prep Chest x-rays should be shielded Why?- Limit exposure for patient. Age doesn't matter! Place around patients waist/on lap/over gonadal area without blocking anatomy of interest Hospital dependent Between 90-125 kVp Between 1-3 mAs Larger patients may need 4 mAs Smaller patients may need 0.9 mAs Pathology changes technique- Additive disease=Higher Tech Destructive disease=Lower tech Bring patient into room AIDET Use 2 identifiers to make sure you have correct patient Remove possible artifacts Position Tube and Bucky Shield Position patient for PA Chest- Upright whenever possible, Center at T7 include all of lungs, no rotation. Set technique for patient Give breathing instructions, take image Radiologist involved? Immobilization Devices ANY QUESTIONS For us? You should know this by now...... Keep a few things in mind with older patient- Communication problems may be an issue with loss of teeth or other issues, Some have trouble hearing, Repeat information if you need to, be patient they are not as fast as us sometimes, confirm their identity sometimes more than once their mental state may be altered. Make sure everyone else is out of the room! Normally, no If you see something you're unsure of call them over to look really fast Don't let patient leave if you see something Remember we can't diagnose... Leave that to the Docs Answers To observe the heart and lungs Illnesses and conditions of heart and lungs that are more common as we age Decreased oxygen levels Continuous coughing SOB Chest pain Fever Shielding Jennifer Bennett, Kelly Carnett, and Sarah Engle There are none for the patient Make sure they have all of their belongings Technologist should wipe down the room and move everything back to original place Portable- Put everything back to how it was when you got there, if patient had 3 pillows give them 3 pillows. Chest x-ray of a Geriatric patient Most common medical imaging exam Small amount of radiation Shows heart, lungs, airway, and chest wall PA and Lateral projections Upright position wanted- shows air/fluid level and depresses diaphragm Used to rule out many respiratory and heart conditions Typically are not used If patient won't stay still AMS patients Sandbags Straps Retrieving Patient (AIDET) Many different diseases can be seen with a chest x-ray Common diseases for elderly patients- Emphysema, Bronchitis, Pneumonia, Pulmonary edema, COPD, Cancer, CHF, Embolism, Aspiration, Asthma, ARDS, Atelectasis, Pneumothorax Prepare the room to meet needs of patient Determine how the images should be taken- ambulatory, wheelchair, or Cart? There is no prep for the patient to do before the exam Refrences Quiz Time! Ambulatory Patient Post Procedure instructions Indications Doing exam in a Cart is similar to a Portable chest x-ray Wheelchair or Cart Geriatric Chest X-Ray Hospital dependent, Usual questions include... Are you a smoker? SOB? Chest pain? History of COPD? Coughing? History of Cancer? How long has this been going on? Surgeries?