Red Blood Cell
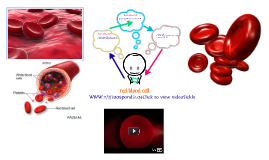
Transcript: Cell differentiation is when a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell Human embryotic stem cells become red blood cells in the bone marrow Red blood cells produce hemoglobin to help transport oxygen through out the body Disease Description Cell Differentiation Red Blood Cells Works Cited "Blood: Red Blood Cells - The Human Heart: An Online Exploration from The Franklin Institute, made possible by Unisys." The Franklin Institute - Home - 215.448.1200. N.p., n.d. Web. 10 Oct. 2012. <http://www.fi.edu/learn/heart/blood/red.html>. "Diseases of red blood cells." UNM - New Mexico's Flagship University | The University of New Mexico. N.p., n.d. Web. 10 Oct. 2012. <http://www.unm.edu/~mpachman/Blood/disRBC.htm>. M.D., Erich Rosenberger. "The functions of red blood cells - by Erich Rosenberger M.D. - Helium." Helium - Where Knowledge Rules. N.p., n.d. Web. 10 Oct. 2012. <http://www.helium.com/items/763669-the-functions-of-red-blood-cells>. "Red Blood Cells Functions, Size, Structure, Life Cycle, Pictures | Healthhype.com." Current Health Articles. N.p., n.d. Web. 14 Oct. 2012. <http://www.healthhype.com/red-blood-cells-functions-size-structure-life-cycle-pictures.html>. MLA formatting by BibMe.org. Red Blood Cells By Yasmeen Shahout and Isabella Burke Malaria- disease contracted from mosquitos Spherocytosis- inherited disease causes Red Blood Cells to swell blocking small blood vessels Thalassemia- inherited disease; shortens a persons life span Anemia- causes a low oxygen transport throughout the body in the blood Polycythemia- Catagorized as a surplus of red blood cells; causes blood to thicken slowing blood flow Functions Diseases that affect the Cell Malaria Spherocytosis Thalassemia Anemia Sickle Cell Polythemia Main function: Carries oxygen throughout the body controls the pH of blood by acting as an acid-base buffer Releases the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, allows water in blood to carry carbon dioxide to lungs where it is dispelled One thing we learned and found interesting while doing this project is the fact that red blood cells do not have a nucleus. In fact, they don't have any organelles besides hemoglobins. This was intersting because all other cells have these things but red blood cells do not. Description 6-8 micrometers in diameter Hemoglobin: protein; carries the oxygen throughout the body; Gives cell its red color Very flexible Biconcave cell Males: 5 million per cubic millimeter of blood Females: 4.5 million per cubic millimeter of blood Lacks nucleus, mitochondria, and ER Life span:120 days