Epidemiology
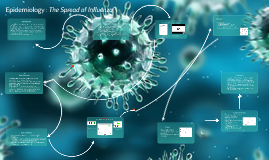
Transcript: Thank you for listening! Common Cold Incidence for common cold is clearly high (anecdotal evidence) BUT, data for hypothesis is lacking Clear incidence of influenza been used as substitute Mortality figures show it is a severe problem facing health service Common Cold is a coronavirus (but can be caused by a rhinovirus too) Grouped with SARS Distinguishable from other common winter diseases such as influenza (an orthomyxovirus) By Aiken Yam & Jack Steadman Public Health England (2012/2013): Influenza activity in UK rose to only low levels Activity was prolonged Reached Levels higher than those seen in 2011/2012 Both children and adults affected Initially marked by outbreaks in schools After Christmas, outbreaks in care homes Brace yourselves... References: 1Isba R, Rapid Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicines [online], Blackwell Publishing, November 2003, available at: https://www.dawsonera.com/abstract/9781405140669. Accessed 14th November 2013. 2ONS, Deaths Registered in England and Wales in 2012 [online], October 2013, available at: http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/vsob1/mortality-statistics--deaths-registered-in-england-and-wales--series-dr-/2012/index.html. Accessed 14th November 2013 3ONS, Deaths Registered in England and Wales in 2011 [online], November 2012, available at: http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/vsob1/mortality-statistics--deaths-registered-in-england-and-wales--series-dr-/2011/index.html. Accessed 14th November 2013 4ONS, Deaths Registered in England and Wales in 2010 [online], October 2011, available at: http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/vsob1/mortality-statistics--deaths-registered-in-england-and-wales--series-dr-/2010/index.html. Accessed 14th November 2013 5ONS, Background and Methodology, 2012-based National Population Projections [online], November 2013, available at: http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/dcp171776_330483.pdf. Accessed 14th November 2013 6ONS, Background and Methodology, 2010-Based National Population Projections [online], October 2011, available at: http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/dcp171776_232313.pdf. Accessed 14th November 2013 7Hemila H, Chalker E, Vitamin C for preventing the common cold [online], January 2013, The Cochrane Library, DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000980.pub4, available at: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD000980.pub4/abstract. Accessed 14th November 2013 8Hemila H, Kaprio J, Albanes D, Heinonen O P, Virtamo J, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, and Beta-Carotene in Relation to Common Cold Incidence in Male Smokers [online], Epidemiology 13;1 January 2002 (pp. 32-37), available at: http://www.jstor.org/stable/3703244?seq=3. Accessed 14th November 2013 9ONS, Excess Winter Mortality in England and Wales, 2011/12 (Provisional) and 2010/2011 (Final) [online], available at: http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/dcp171778_288362.pdf. Accessed 14th November 2013 10Public Health England, Surveillance of influenza and other respiratory viruses, including novel respiratory viruses in the UK: Winter 2012-13 [online] http://www.hpa.org.uk/webw/HPAweb&HPAwebStandard/HPAweb_C/1317139320524. Accessed 14th November 2013 Epidemiology Major cause of visits to a doctor in high-income countries and of absenteeism from work and school. Over 200 viruses cause common cold symptoms Symptoms vary Antibiotics are useless making other treatment options a substantial public health interest Winter is Coming...