Concept Map Template
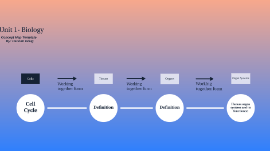
Transcript: Organ Systems Tissues Working together form Unit 1- Biology Working together form Organs Cells Concept Map Template By: Hannah Greig Working together form Why is this important? The cell cycle's important because without it we wouldn't get new cells for growth and repair. Humans would not survive without the cell cycle. Cell Cycle Cell Cycle The phases of Mitosis; Prophase: The cell starts to break down structures and build others up, setting the stage for division of chromosomes. And then the spindle begins to "capture" chromosomes. Metaphase: The spindle has captured all the chromosomes and lined them up at the middle of the cell, ready to divide. Anaphase: The sister chromatids seperate from each other and are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell. Telophase: The cell is nearly done dividing, and it starts to re-establish its normal structures as cytokinesis takes place. What happens when it's uncontrolled? When mitosis gets out of control, cells divisions are being made continuously, without an end point. As a result, this problem could lead to various types of cancer. Early Frog Embryo Cell Specialization and Differentiation Cell Specialization and Differentiation The cells are not yet differentiated into distinct cell types. Cells specialize to form different tissues and organs (the eye and heart are visible). Plant vs Animal Plant vs Animal Both are eukaryotic cells. Centrosomes and lysosome are found in animal cells. Animal cells don't have a cell wall or chloroplasts. Round shaped. Cilia is present. Centrosomes and lysosomes don't exist within plant cells. Plant cells do have a cell wall or chloroplasts. Rectangular shaped Most plant cells don't contain cilia. Animal cell Plant cell Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organ. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. Definition Definition Epithelial tissue covers the body surface and forms the lining for most internal cavities. Connective tissue is the most abundant and the most widely distributed of the tissues. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, and cardiac Nerve tissue is composed of specialized cells which not only receive stimuli but also conduct impulses to form all parts of the body. 4 types of tissues in the human body 4 types of tissues in the human body A part of an organism that is typically self-contained and has specific vital function, such as the heart or liver in humans. Definition Definition Skin Brain Heart Liver Pancreas Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Lungs Kidneys At least 10 examples At least 10 examples Skeletal system provides support and structure, stores calcium, minerals, fats, marrow. Integumentary system provides protection regulates body temp, prevents water loss. Muscle system provides body movement and generates heat when muscles contact. Nervous system controls body movement, consciousness, intelligence, memory. Endocrine system secretes hormones which regulate body and cellular growth, chemical levels in the body, and reproductive functions. Circulatory system pumps blood to distribute hormones, nutrients and gases and removes wastes. Lymphatic system transports and filters lymph and initiates immune response. Digestive system mechanically and chemically breakdowns food materials, absorbs nutrients and expels waste. Respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of gases within the body between blood and lungs. Urinary system filters the blood and removes waste from it concentrates waste into urine and expels urine from body Reproductive system produces sex cells, hormones and when in conjunction allows for fertilization. Human organ systems and its function(s) Human organ systems and its function(s) Cardiovascular and respiratory system. Digestive and excretory systems. Endocrine and Immune systems. Integumentary and nervous systems. Skeletal and muscular systems. How organ systems interact with eachother How organ systems interact with eachother